What is a stethoscope?
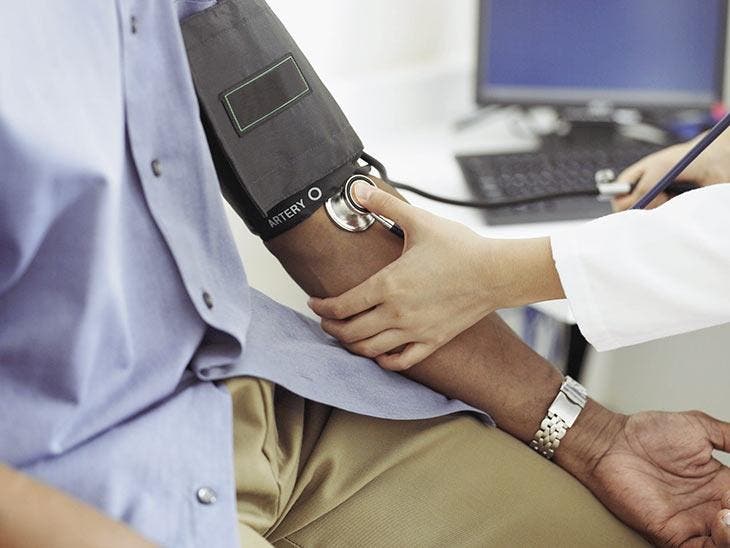
Device overview
The stethoscope is a device that transmits and amplifies resonance noises. Designed for the first time in 1829, it was in 1851 that the first model of this device was born.
Originally, the instrument was adored for its functionality even if it was very fragile. Thanks to a series of improvements, we find the device as known today.
How the stethoscope works
The principle of operation of the stethoscope is simple. The sound is picked up by a bell or membrane that transmits it to the user’s ears via a duct. However, the mechanism of operation varies depending on the model. As proof, for the electronic stethoscope, a microphone is essential.
Choosing a stethoscope
Choosing a stethoscope is like any device, a task to be taken seriously. It is not enough to obtain any kind of model to have the desired results.
Before touching, it is necessary to take into account the use that will be made of the device. Indeed, each medical profession makes use of a very specific model.
Then, the ideal model is to be taken into account. Indeed, apart from the classic stethoscope, there are electronic models, such as those offered by the manufacturer Realme.
Finally, the quality of the materials is a significant criterion. It defines the reliability of the accessory as well as its durability.
What are the components of a stethoscope?
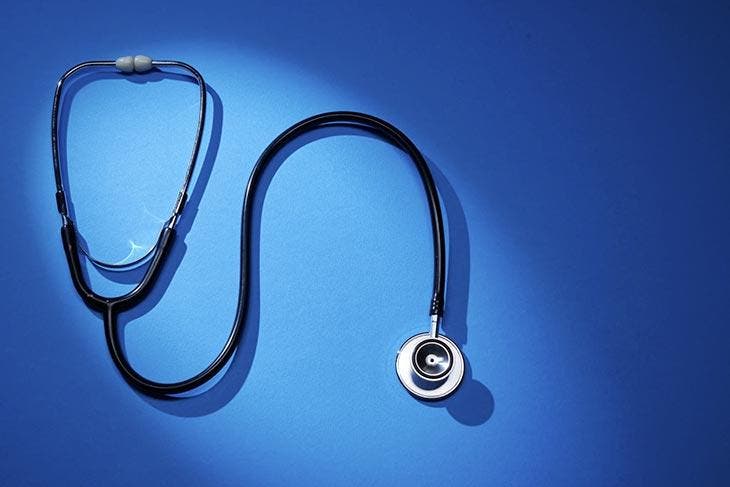
The pavilion
The pavilion is an important and sensitive part of the device. It is responsible for capturing the sounds and is therefore responsible for the quality of listening. There are several models of pavilions found in a stethoscope: single pavilions and double pavilions (equipped with a membrane and a bell).
The membrane is used to listen to high-frequency sounds such as ventilatory noises. As for the bell, it corresponds to low frequencies such as the heartbeat.
The basis
The base is the support of the pavilion. It is a rigid part that is connected to the stethoscope tube. It plays several roles, such as the choice of mode of use. Thus, with this instrument, it is possible to switch from low frequencies to high frequencies and vice versa.
The tube
The tube is nothing but the receptacle of the pipe. It splits into two to allow biauricular listening. It is also a rigid (metal) and non-malleable part that consists of two tubes supported by a tension spring.
The lyre
The lyre manages the spacing between the listening tips to adapt them to the user. It is an indispensable part that ensures comfort.
The tips
The tips are the parts reserved for the hollows of the ears. They are comparable to those of smartphone headphones or MP3s. For hygienic reasons, the tips are used by one doctor at a time.





